1
Feature Story
After switching from a 1080ti to a 4090, this programmer wants to save people by offering FREE services
Feb 13, 2024 · howardchen.substack.com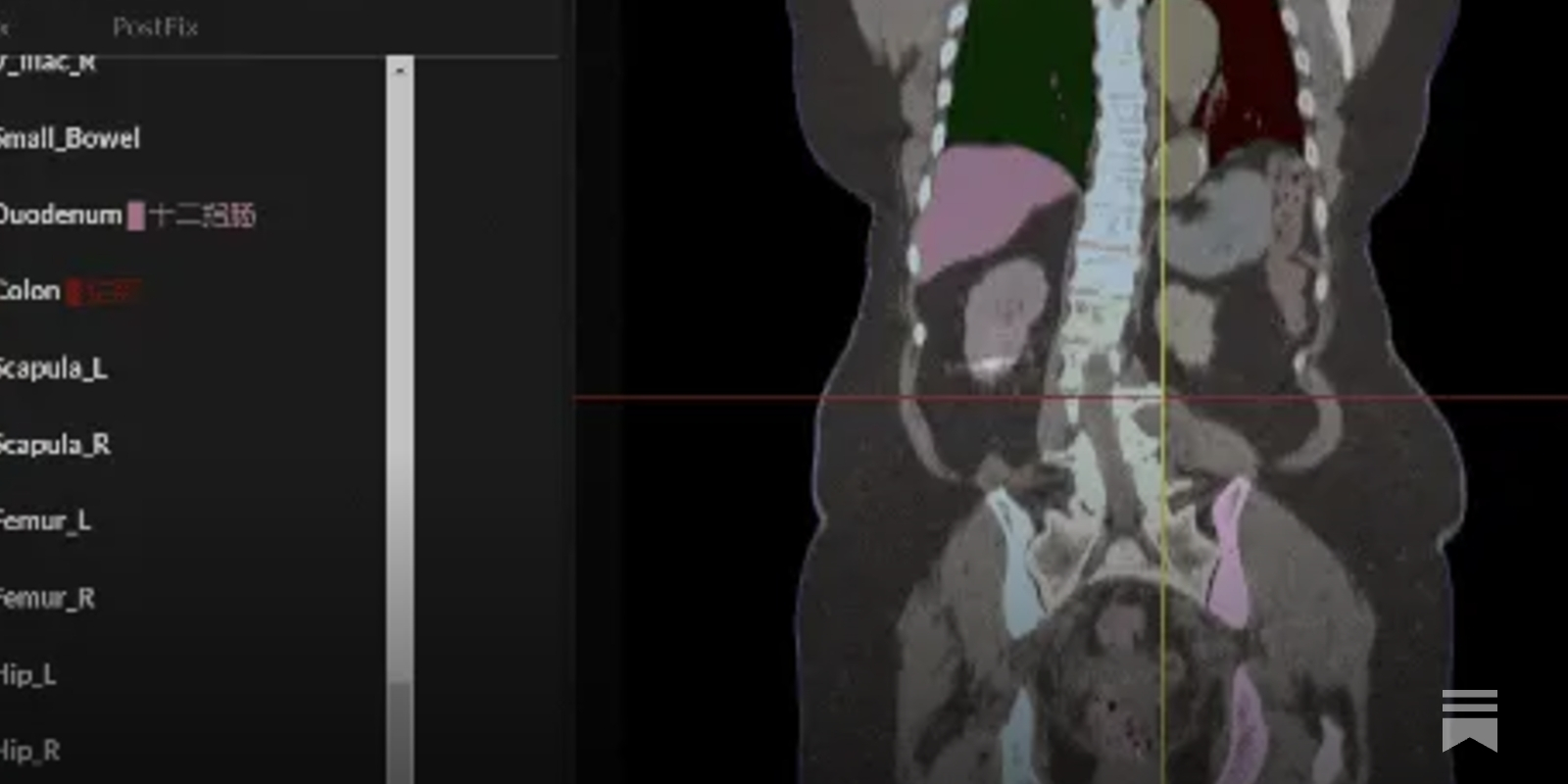
The platform has been tested by doctors in countries with scarce medical resources, such as India, Lebanon, Tashkent, and Pakistan, and has been found to significantly reduce the time spent manually outlining tumors, enabling the treatment of more patients. Coolwulf's future plans for NeuralRad include making it a collaborative tool, similar to Figma, that allows physicians, radiation therapists, dosimetrists, and nurses to operate the software simultaneously. He also aims to use clinical trial data to train a model capable of providing various cancer treatment plans, including information on the success rate of each plan and recommendations for the choice of radiation therapy equipment.
Key takeaways
- Coolwulf Jiang Hao, a physicist and programmer, has developed NeuralRad, a free cloud service that uses AI to identify and segment organs and tumors from CT or MRI scans.
- The platform, which is still in its Beta phase, can automatically segment whole body organs and outline brain tumors, significantly reducing the time and effort required by doctors.
- NeuralRad has been selected by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) for a project in the IAEA 2023 Medical Physics Artificial Intelligence Workshop, and has received interest from various countries and organizations, including Harvard Medical School.
- Coolwulf's vision is to make AI technology accessible to all, especially in third-world countries with limited resources, by offering the platform for free and setting up cloud servers for easy and cost-effective use.