1
Feature Story
Building effective agents
Dec 19, 2024 · anthropic.com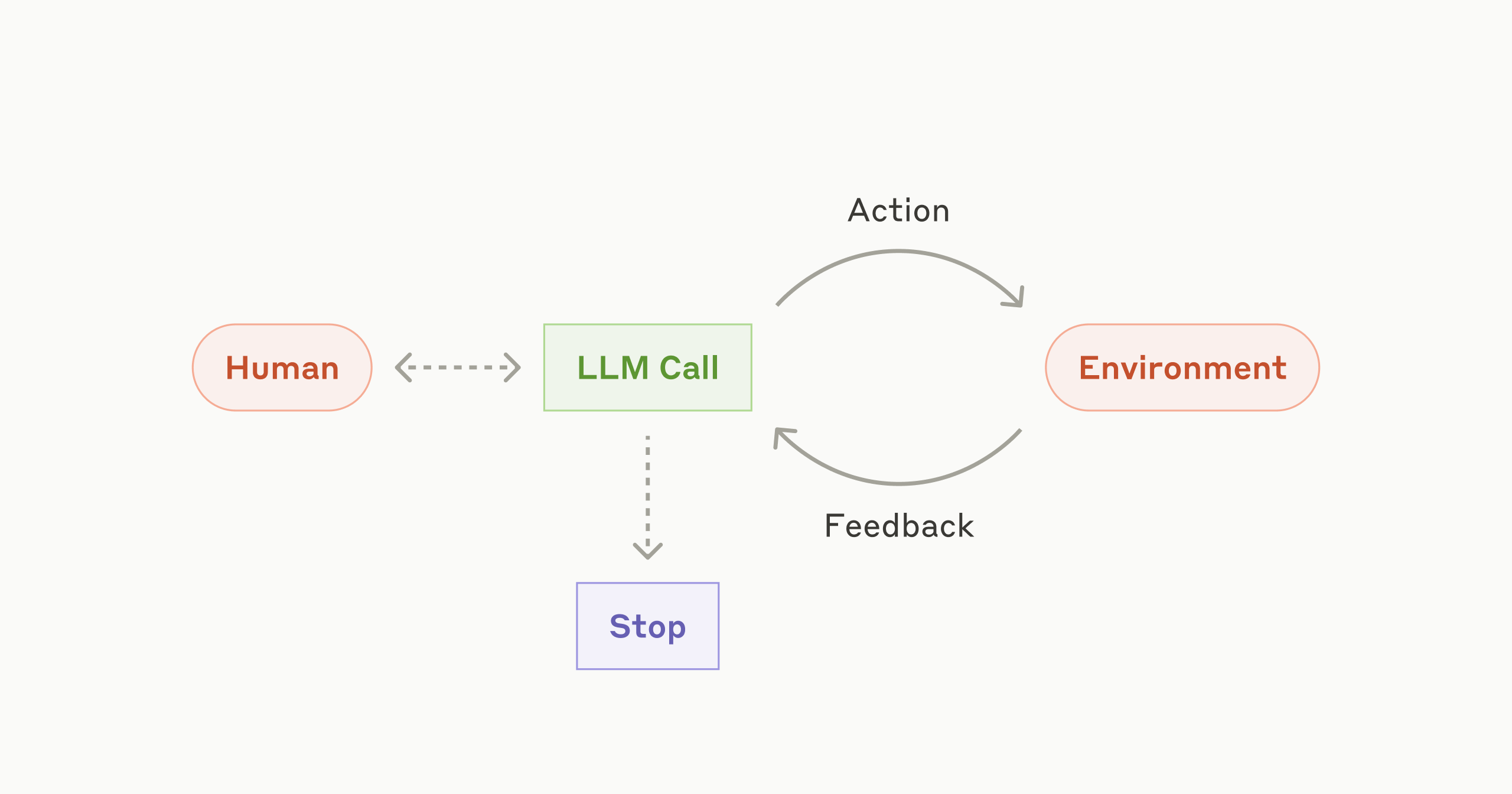
The article also highlights the importance of understanding frameworks and suggests starting with direct LLM API usage. It provides insights into building blocks like augmented LLMs and emphasizes the need for well-documented interfaces. The article concludes with practical applications of agents in customer support and coding, where agents add value through conversation and action, and stresses the importance of prompt engineering for tool integration. The key takeaway is to build the right system for specific needs, maintaining simplicity, transparency, and thorough testing.
Key takeaways
- Successful LLM agent implementations often rely on simple, composable patterns rather than complex frameworks, emphasizing the importance of starting with basic solutions and increasing complexity only when necessary.
- Agents are distinguished from workflows by their ability to dynamically direct their own processes and tool usage, making them suitable for tasks requiring flexibility and model-driven decision-making at scale.
- Frameworks can simplify the implementation of agentic systems but may add unnecessary complexity; developers should understand the underlying code and consider using LLM APIs directly for simpler tasks.
- Effective tool integration is crucial for agentic systems, requiring careful prompt engineering to ensure tools are intuitive and easy for models to use, akin to designing human-computer interfaces.