1
Feature Story
Combining Thermodynamics and Diffusion Models for Collision-Free Robot Motion Planning
Oct 22, 2023 · aimodels.substack.com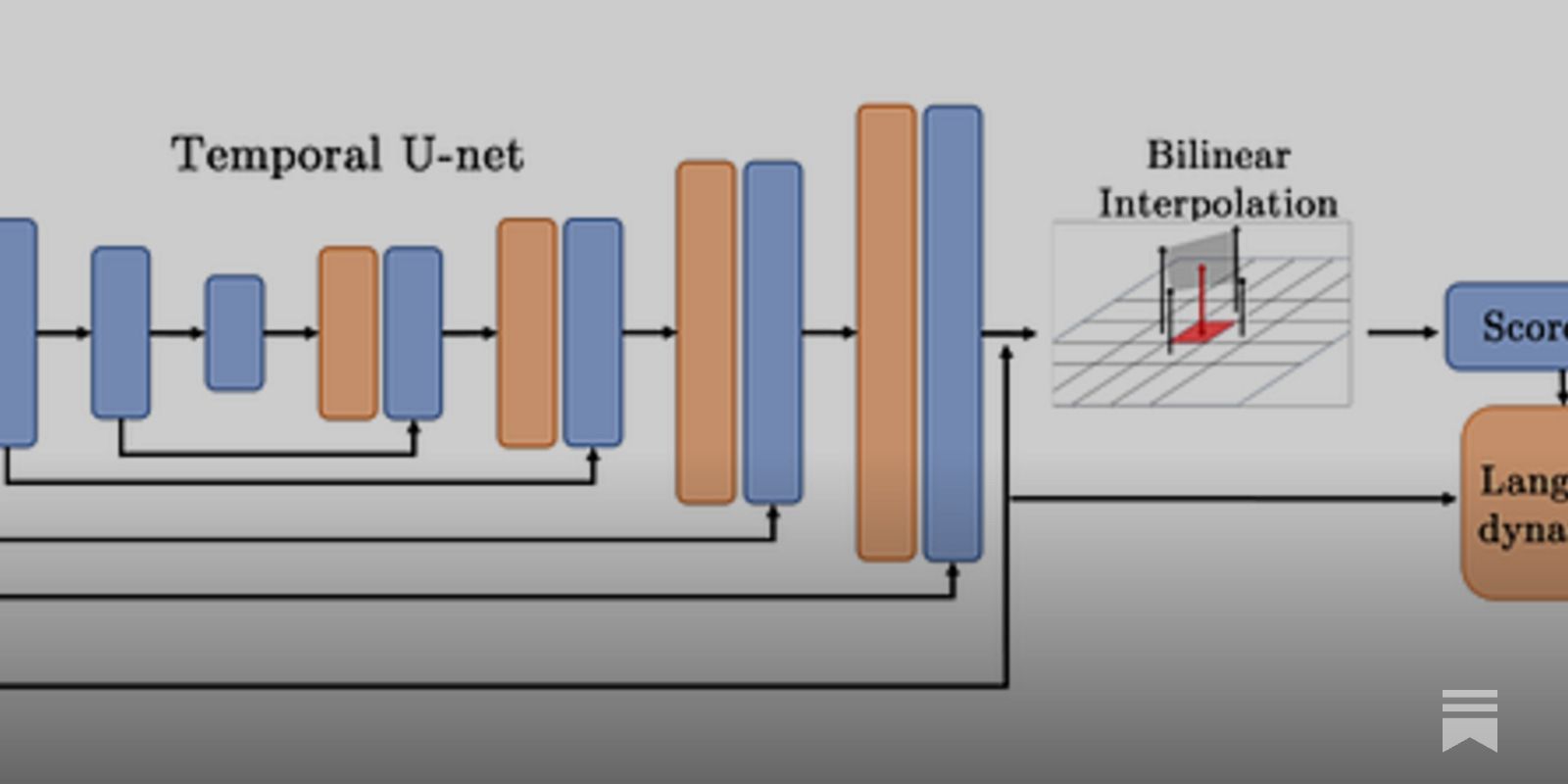
The research addresses several challenges in the field of robotics, including mapping requirements and brittleness to unexpected obstacles. Most navigation solutions require an accurate 2D or 3D map of the environment beforehand, limiting robots to narrow industrial settings with fixed infrastructure. Additionally, robots struggle to respond in real-time to novel obstacles and changes in mapped environments. The researchers' method could potentially be applied to various fields such as warehouse robotics, manufacturing, and self-driving cars.
Key takeaways
- Researchers from Yonsei University and UC Berkeley have developed an AI technique that improves robot navigation in complex environments by using a tailored diffusion model to generate collision-free motion plans.
- The method is inspired by the behavior of heat avoiding insulators, and could be applied in fields such as warehouse robotics, manufacturing, and self-driving cars.
- Current challenges in robot navigation include the need for accurate mapping of the environment, which is often infeasible in dynamic spaces, and the brittleness of robots to unexpected obstacles, which can lead to catastrophic failures.
- The new method aims to overcome these challenges and make autonomous navigation more practical and scalable, enabling robots to handle changing environments cluttered with both static and dynamic obstacles.