1
Feature Story
Infinite context windows? LLMs can be extended to infinite sequence lengths without fine-tuning
Oct 03, 2023 · notes.aimodels.fyi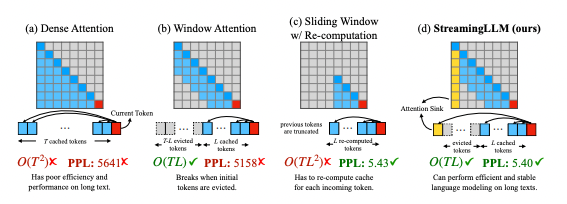
However, there are challenges in deploying LLMs for streaming, including memory overhead and performance decline. A technique called windowed attention was used to mitigate memory overhead, but it led to a drastic drop in the model's predictive performance. StreamingLLM addresses this by maintaining a small cache containing initial "sink" tokens along with the most recent tokens. This allows LLMs to handle context lengths exceeding 4 million tokens, a 1000x increase over their training corpus. Despite these advancements, concerns around bias, transparency, and responsible AI remain when deploying such powerful models.
Key takeaways
- Researchers from MIT, Meta AI, and Carnegie Mellon have proposed StreamingLLM, a framework that enables large language models (LLMs) to handle infinite-length language modeling without expensive fine-tuning.
- StreamingLLM overcomes the limitations of LLMs by maintaining a small cache containing initial 'sink' tokens and the most recent tokens, allowing the models to handle context lengths exceeding 4 million tokens.
- StreamingLLM achieved up to 22x lower latency than prior approaches while retaining comparable perplexity, potentially enabling practical streaming deployment of LLMs in interactive AI systems.
- Despite the technical advancements, concerns around bias, transparency, and responsible AI remain when deploying such powerful models interacting with humans.