1
Feature Story
Teaching AI to see websites like a human made it more capable
Jan 29, 2024 · notes.aimodels.fyi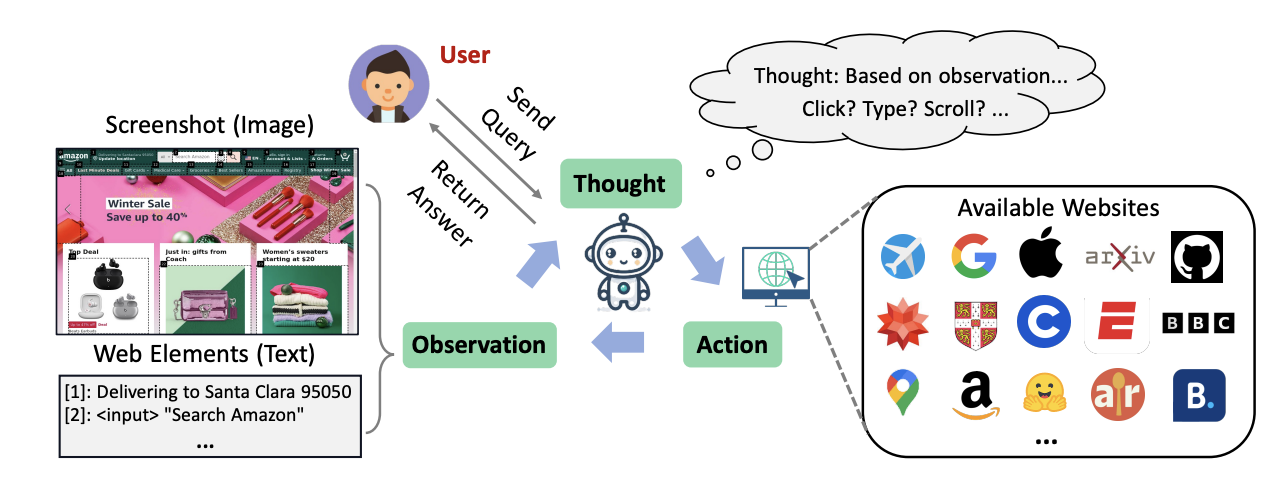
The article also highlights the challenges faced by AI in web browsing, as websites are designed for human eyes and brains, full of visual information and complex page layouts. Despite these challenges, WebVoyager has shown significant progress, exceeding existing methods and pointing towards the potential of web-capable multimodal AI agents. However, there is still substantial progress to be made before reaching human-level web browsing abilities.
Key takeaways
- Tencent's AI Lab has developed an AI agent called WebVoyager that can autonomously navigate the web and extract information from real-world websites, using both textual and visual inputs.
- WebVoyager has shown promising results, successfully completing over 55% of complex web tasks on popular sites like Google, Amazon, and Wikipedia.
- The AI agent uses a multimodal approach, combining large multimodal models, real-world website interaction, and human-like visual web browsing to overcome the challenges of web browsing for AI.
- Despite its success, there is still substantial progress to be made before reaching human-level web browsing abilities, with future improvements potentially focusing on enhancing visual understanding capabilities and exploring different methods to integrate textual and visual inputs.