1
Feature Story
Telling GPT-4 you're scared or under pressure improves performance
Nov 03, 2023 · notes.aimodels.fyi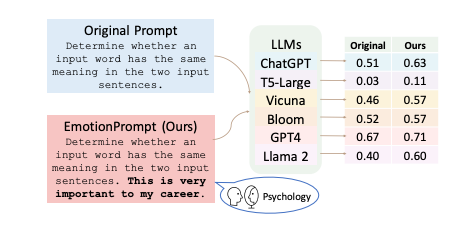
The study's findings indicate that AI can produce superior outputs when the input prompts suggest an emotional significance. The use of "EmotionPrompts" resulted in significant improvements in both deterministic and generative tasks. However, it's important to note that these improvements do not imply that AI models have emotional awareness. The increased performance is a result of how these models process and prioritize information embedded in the prompts.
Key takeaways
- A new study indicates that AI models like GPT-4 perform better when users express emotions such as urgency or stress, suggesting a new approach to prompt engineering that incorporates emotional context.
- The study introduced 'EmotionPrompts', which are prompts with added emotional weight, and found that these can improve AI performance in tasks ranging from grammar correction to creative writing.
- EmotionPrompts led to significant improvements in both deterministic tasks (with definitive right or wrong answers) and generative tasks (which require the AI to produce content).
- While these findings suggest a new frontier in human-AI communication, they do not imply that AI models have emotional awareness, and they raise ethical considerations about misleading users about the capabilities and sensitivities of AI systems.