1
Feature Story
The Download: gene-edited pig liver transplants, and AI to fight apartheid
Jan 19, 2024 · technologyreview.com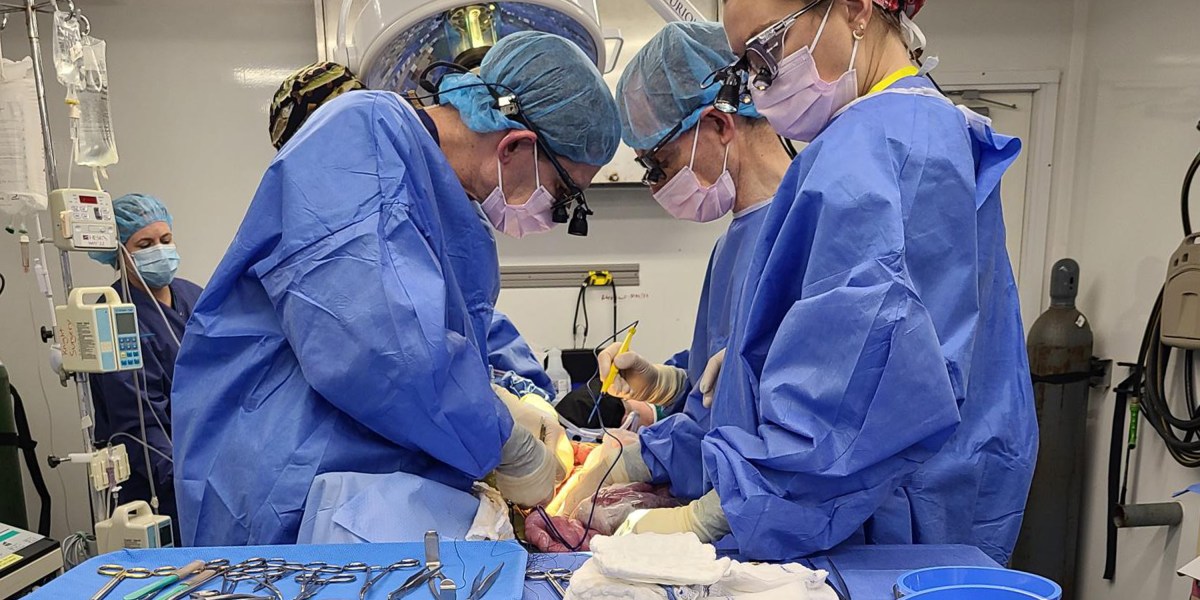
In other news, Meta has announced its intention to create artificial general intelligence, joining the ranks of OpenAI and Google DeepMind. The article also discusses the potential flaws in AI testing, with claims that large language models can pass cognitive tests designed for humans, feeding into the hype that these machines could replace white-collar jobs. However, there is little consensus on what these results truly mean.
Key takeaways
- A brain-dead man was attached to a gene-edited pig liver for three days in an experiment to help people survive acute liver failure.
- Raesetje Sefala is using computer vision tools and satellite images to analyze and hopefully reverse the impacts of racial segregation in housing in South Africa.
- The first gene-editing treatment has been developed to cure the symptoms of sickle-cell disease, a condition that affects 1 in 4,000 people in the US, nearly all of them African-American.
- AI hype is built on high test scores, but there's little agreement on what those results really mean, raising questions about the future of AI in white-collar jobs.