1
Feature Story
Up to 17% of AI conference reviews now written by AI
Mar 27, 2024 · aimodels.substack.com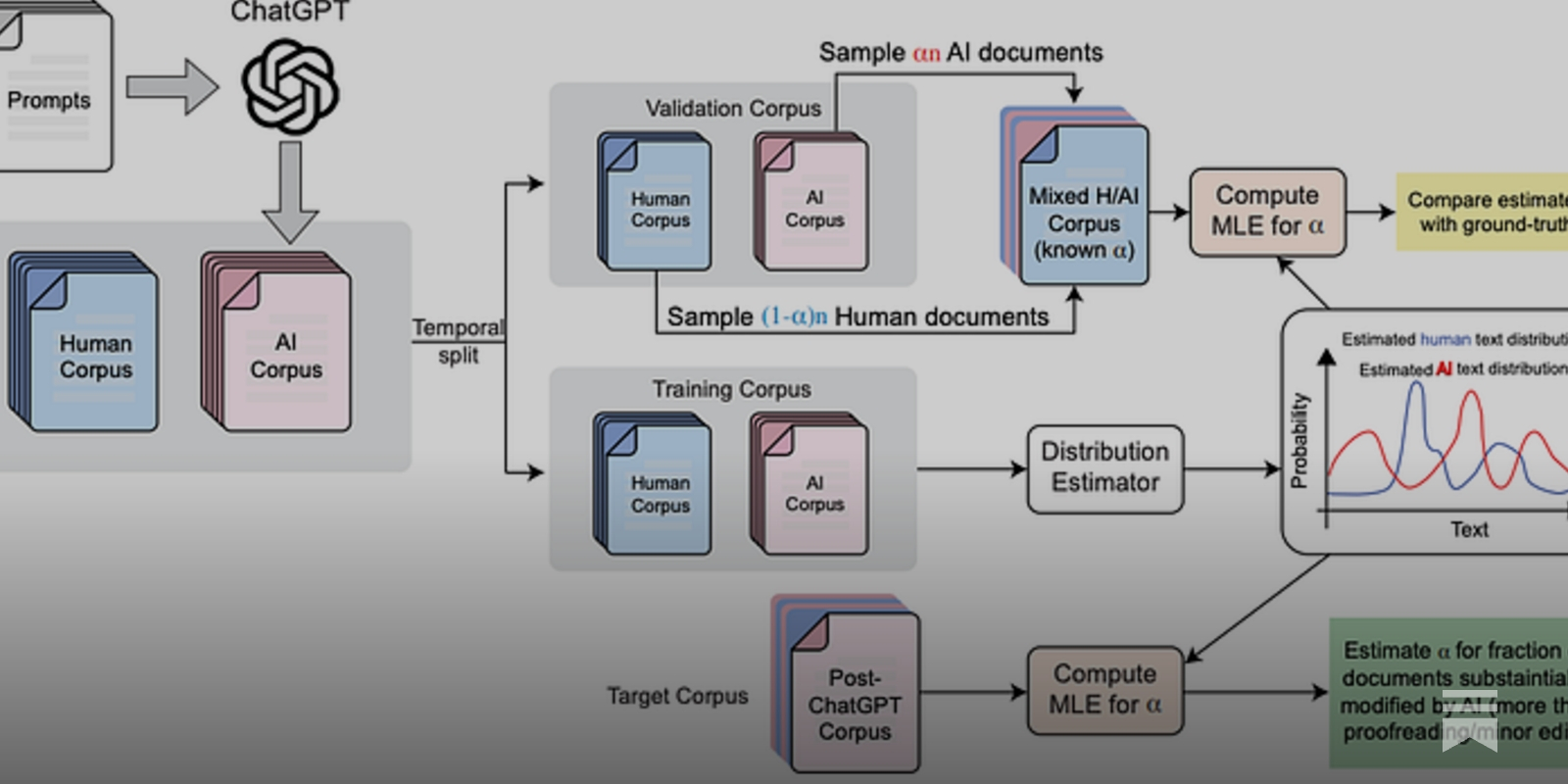
The authors express concern that the increasing use of AI in peer reviews could compromise the quality control of scientific research. They suggest that the scientific community needs to establish norms and expectations for using AI in peer review and consider how AI could reshape scientific reward structures. The study also highlights the need for ongoing monitoring of AI's influence in scientific research and the development of systems and incentives to ensure AI tools enhance, rather than erode, the quality and trustworthiness of science.
Key takeaways
- A team of researchers has developed a method to detect the presence of AI-generated content in scientific peer reviews, revealing a significant increase in the use of AI writing tools in the review process of major machine learning conferences.
- The study proposes a new method called 'distributional GPT quantification' to estimate the fraction of text that has been substantially modified or generated by AI in a large corpus.
- The researchers found that after the release of ChatGPT in late 2022, the prevalence of AI-generated content in reviews for major AI conferences increased significantly, with estimates ranging from 6.5% to 16.9% depending on the conference.
- The study also found that AI-generated reviews are more likely to be submitted close to the deadline, contain fewer scholarly citations, come from reviewers who engage less in the rebuttal process, and sound more alike, among other factors.