1
Feature Story
You can predict disease progression by modeling health data in latent space
Nov 15, 2023 · notes.aimodels.fyi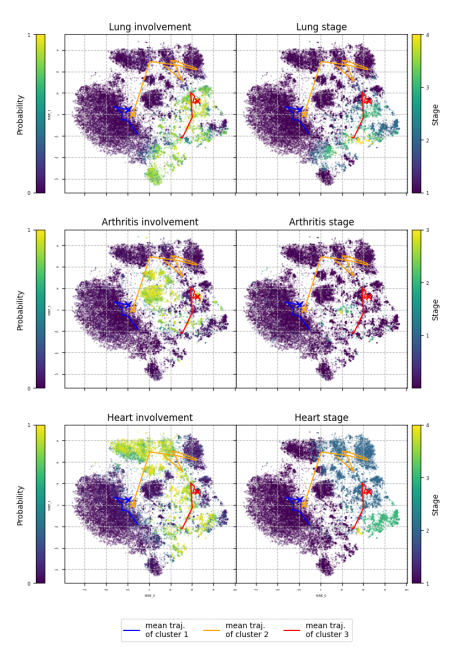
The study suggests that deep generative models, combined with expert knowledge, could provide new insights into systemic sclerosis progression. However, further work is needed to validate the model's performance across diverse cohorts and establish its clinical utility. If successful, this approach could enable precision prognosis, decision support, and personalized treatment for systemic sclerosis, potentially improving patient outcomes through enhanced monitoring, risk stratification, and tailored interventions.
Key takeaways
- A recent study proposes an innovative deep-learning technique for modeling systemic sclerosis progression over time, using deep generative models and medical knowledge to reveal novel phenotypes and progression pathways.
- The research team developed an advanced method using a specific type of conditional latent variable model known as a variational autoencoder. This model identifies and learns patterns in the data without any predefined labels or targets.
- The model was evaluated using real-world data from the EUSTAR cohort, which consists of data from over 5000 patients with systemic sclerosis. The model demonstrated a notable ability to predict individualized disease progression patterns and the associated uncertainty for each patient.
- While the study provides promising evidence, significant work remains to validate model performance across diverse cohorts, determine appropriate medical concept definitions, and establish clinical utility. If successful, this approach could enable precision prognosis, decision support, and treatment personalization for systemic sclerosis.